Your Function of cuticle in plants images are ready. Function of cuticle in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Function of cuticle in plants files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for function of cuticle in plants pictures information linked to the function of cuticle in plants topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Function Of Cuticle In Plants. The structure and chemical composition of the cuticle vary among plant organs and species, and have been studied since the 19th century using a wide range of techniques [3,4].in consequence, various interpretations of the cuticle structure and accompanying terminology have been introduced over years [3,4,5].according to a “classic”. Learn the function, concept, and application of the cuticle of the leaf in protecting the. The plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection against desiccation and external environmental stresses. Rose� department of plant biology, cornell university, ithaca, new york 14853 the plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection
 01 plants part 2 (slideshare) From slideshare.net
01 plants part 2 (slideshare) From slideshare.net
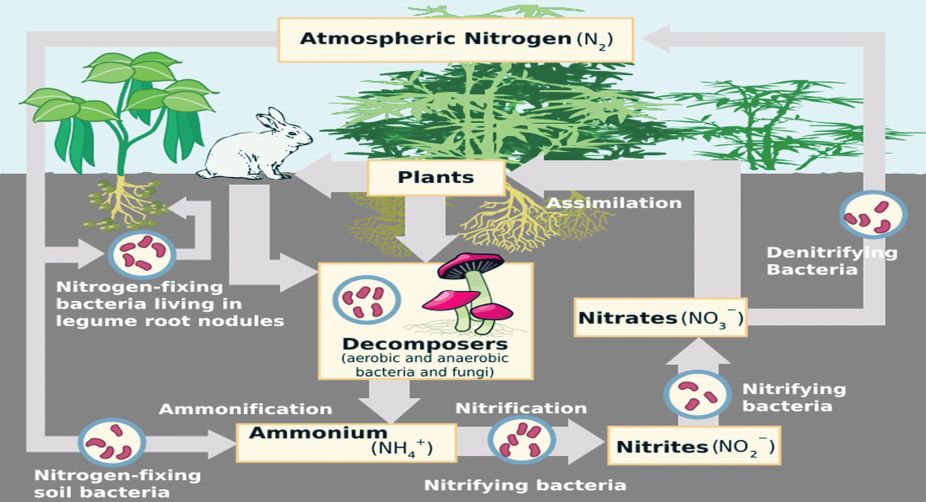
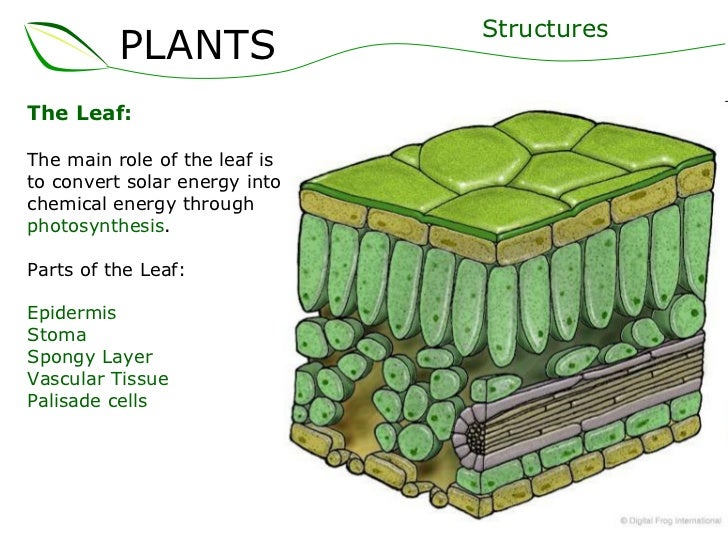
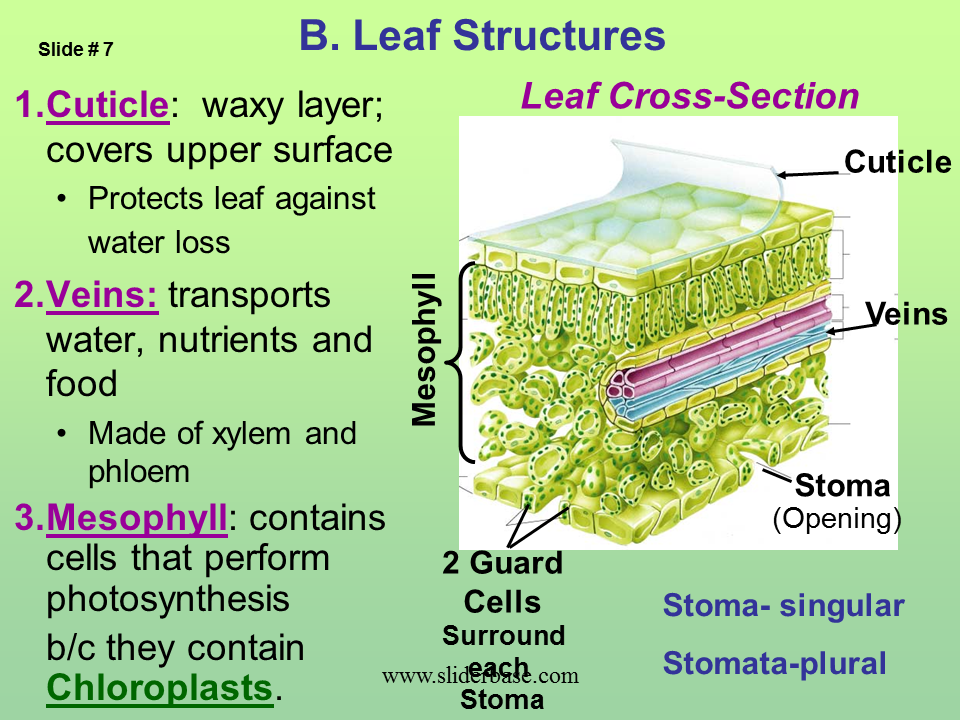
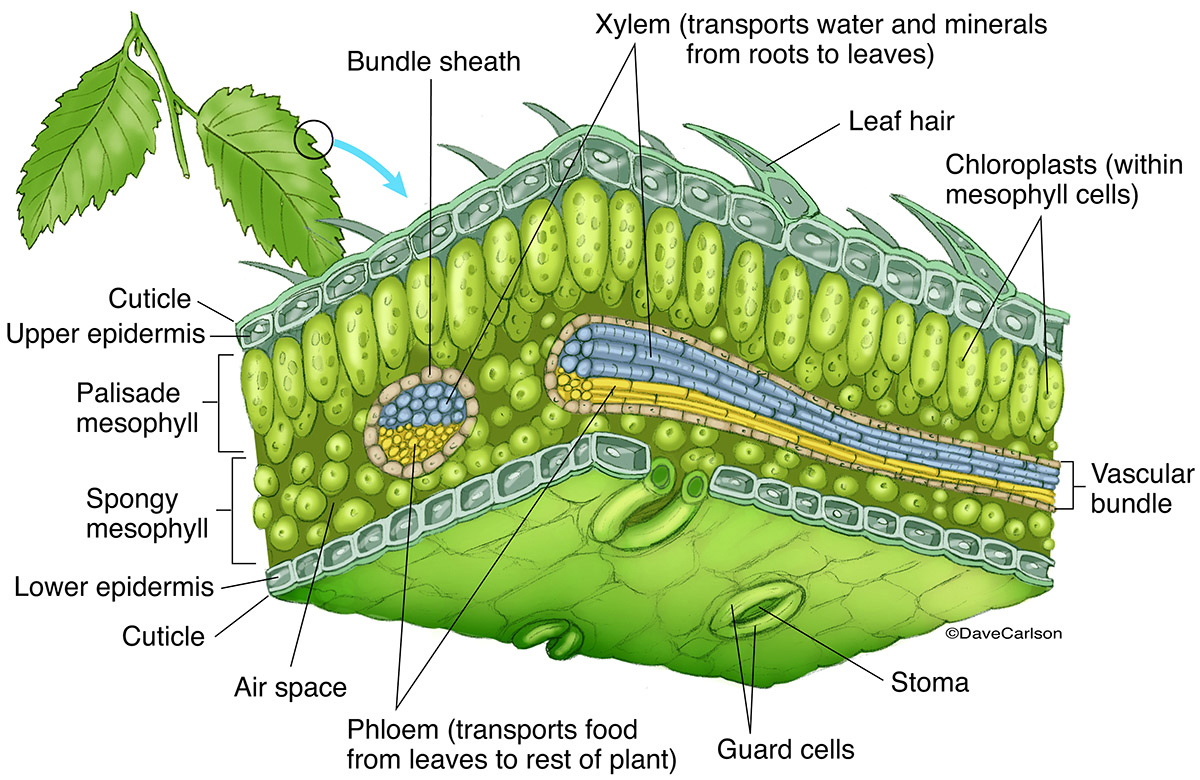
Overlooked water loss in plants could throw off climate. Leaf name description function cuticle thin waxy layer on the epidermis reduces water loss upper epidermis thin and transparent cells with no chloroplasts present allow light to pass through prevent microorganisms from entering (barrier to disease) helps keep leaf’s shape palisade mesophyll long with many chloroplasts main region for photosynthesis chloroplast. The cuticle reduces the rate of water loss from the leaf surface. The cuticle is widely discharged by the epidermis and helps in preventing water loss and infection by parasites. It also prevents external water and solutes from entering the tissues. The function of a cuticle in a plant is similar to what the skin does to humans.
Its prevents water loss and contamination of the plants tissue with external water, dirt and microorganisms.
On leaves, the cuticle is 1/10 to 14 micrometers thick. Topical review on cuticle synthesis and function the formation and function of plant cuticles1 trevor h. On leaves, the cuticle is 1/10 to 14 micrometers thick. The cuticle is widely discharged by the epidermis and helps in preventing water loss and infection by parasites. Relax rejuvenate & rejoice in 4 star luxury september 12, 2017. Along with this, it prevents the entering of the water molecules and the solutes from the external environment.
 Source: opened.cuny.edu
Source: opened.cuny.edu
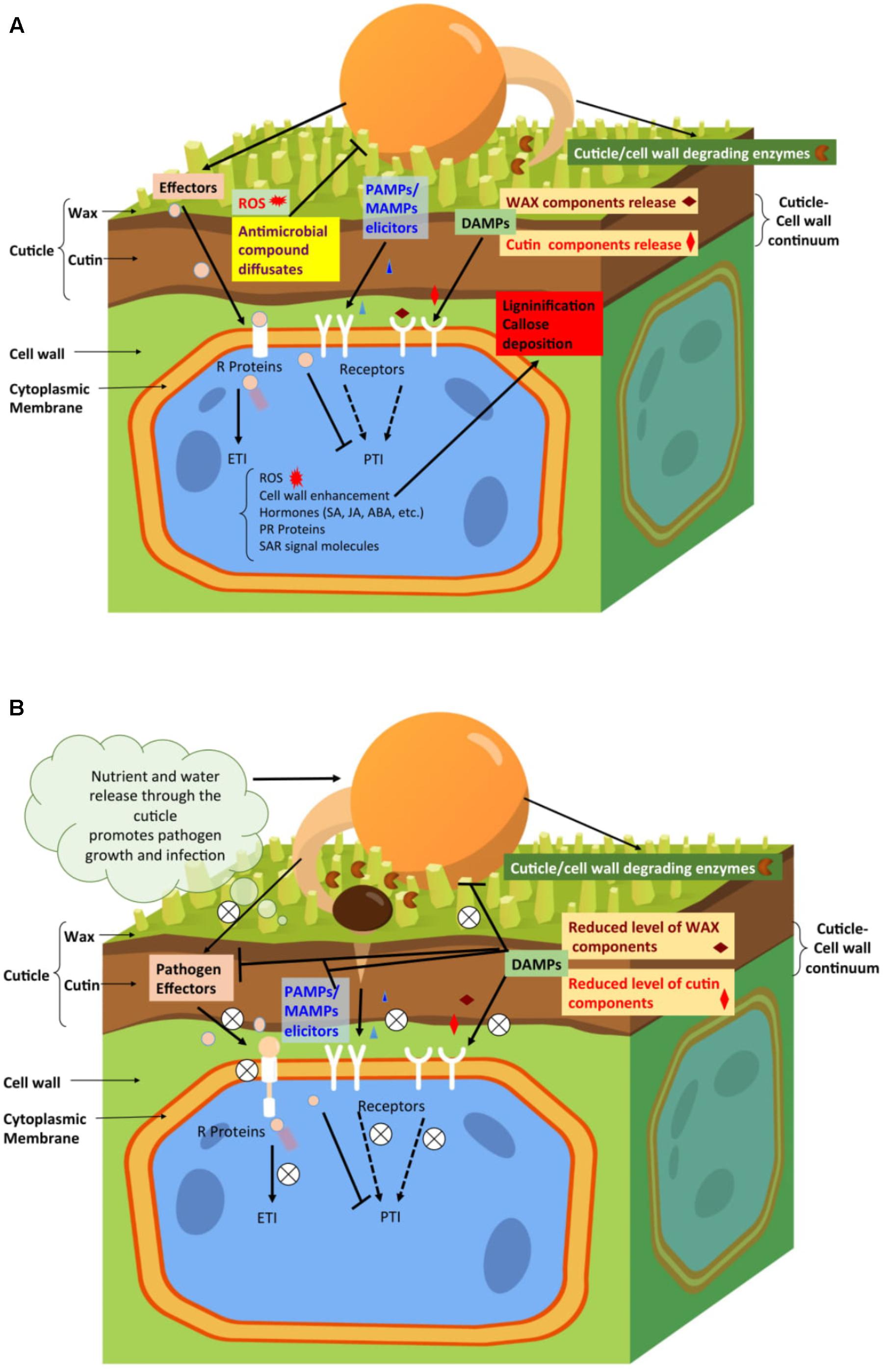
What is the main function of cuticle in plants brainly? The past decade has seen considerable progress in assembling models for the biosynthesis of its two major compone. The function of a cuticle in a plant is similar to what the skin does to humans. What is the main function of cuticle in plants brainly? One of the most fascinating features of the cuticle is that it is laid down, de novo, on the surface of the l1 (epidermal) cell layer during early embryo development and then grows continuously with the plant, maintaining its function as a diffusion barrier.during development, the composition, ultrastructure, and properties of the cuticle change extensively in a manner.
 Source: brainly.in
Source: brainly.in
What is the main function of cuticle in plants brainly? Recent progress in the biochemistry and molecular biology of cuticle synthesis and function highlights major questions that will drive future research in this field. The plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection. To see more answers head over to college study guides. Likewise, oxygen produced during photosynthesis can only pass out of the leaf through the opened stomata.

It also prevents external water and solutes from entering the tissues. Its prevents water loss and contamination of the plants tissue with external water, dirt and microorganisms. The function of a cuticle in a plant is similar to what the skin does to humans. The cuticle is widely discharged by the epidermis and helps in preventing water loss and infection by parasites. In all types of plants, the cuticle is the layer of wax and cutin that covers the outermost surfaces of a plant.
 Source: hubpages.com
Source: hubpages.com
Function of cuticle in plants Function of cuticle in plants To see more answers head over to college study guides. Some plants have adapted to have a cuticle, which is the waxy layer covering the surface of the plant. A) carbohydrates and oxygen b) sugar and carbon dioxide c) starch and carbon dioxide d) chlorophyll and radiant energy 4.
 Source: toppr.com
Overlooked water loss in plants could throw off climate. Protect and cover upper and lower leaf surfaces, prevent water loss and seepage. The cuticle is widely discharged by the epidermis and helps in preventing water loss and infection by parasites. The cuticle is where all the chloroplasts are found, it is used for photosynthesis the cuticle is a hydrophobic layer that protects the leaf photosynthesis is the process in which plants produce: Cuticles, which are composed of a variety of aliphatic molecules, impregnate epidermal cell walls forming diffusion barriers that cover almost all the aerial surfaces in higher plants.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Function of cuticle in plants The plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection. The plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection against desiccation and external environmental stresses. Likewise, oxygen produced during photosynthesis can only pass out of the leaf through the opened stomata. The primary function of the plant cuticle is as a water permeability barrier that prevents the evaporation of water from the epidermal surface.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Learn the function, concept, and application of the cuticle of the leaf in protecting the. It protects plants against drought, extreme temperatures, uv radiation, chemical attack, mechanical injuries, and pathogen/pest infection. The plant cuticle has been traditionally considered to be an independent structure, distinct from the polysaccharide cell wall underneath (yeats and rose, 2013), but the two structures are physically associated and have some overlapping functions. Learn the function, concept, and application of the cuticle of the leaf in protecting the. One of the most fascinating features of the cuticle is that it is laid down, de novo, on the surface of the l1 (epidermal) cell layer during early embryo development and then grows continuously with the plant, maintaining its function as a diffusion barrier.during development, the composition, ultrastructure, and properties of the cuticle change extensively in a manner.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
What are the functions of the cuticle and stomata? Cuticle thickness varies, depending on plant type and the plant parts it covers. In all types of plants, the cuticle is the layer of wax and cutin that covers the outermost surfaces of a plant. Learn the function, concept, and application of the cuticle of the leaf in protecting the. The formation and function of plant cuticles1.
Likewise, oxygen produced during photosynthesis can only pass out of the leaf through the opened stomata. Function of cuticle in plants accounting courses near me family and friends day activities how much is $50,000 a year per month function of cuticle in plants home Other leaves may have small hairs (trichomes) on the leaf surface. On leaves, the cuticle is 1/10 to 14 micrometers thick. Protect and cover upper and lower leaf surfaces, prevent water loss and seepage.
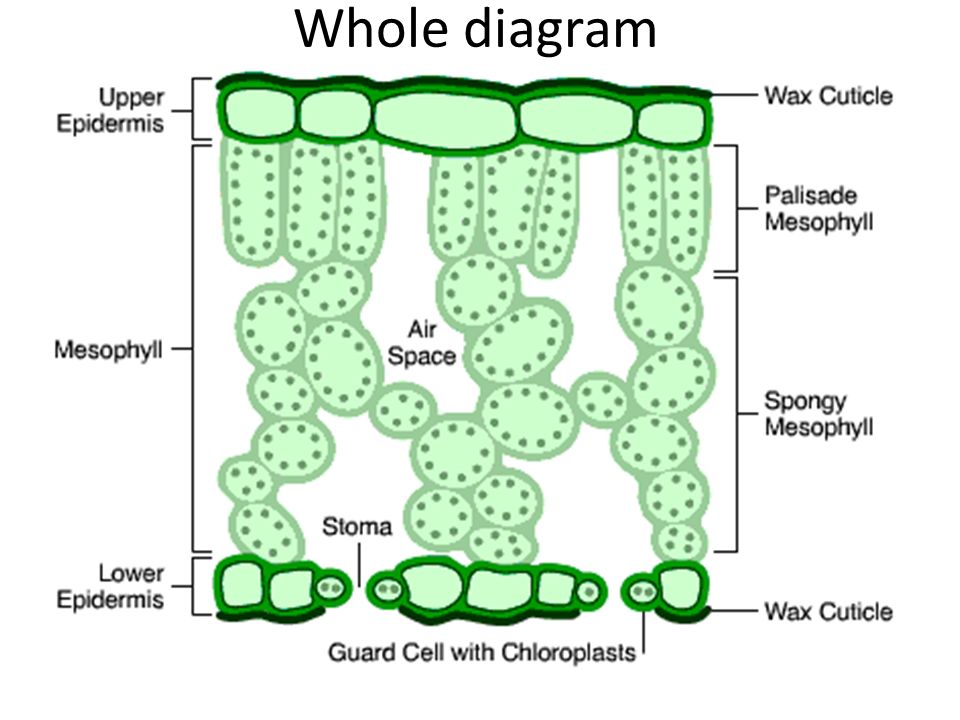
What are the functions of the cuticle and stomata? The cuticle is widely discharged by the epidermis and helps in preventing water loss and infection by parasites. The cuticle reduces the rate of water loss from the leaf surface. The past decade has seen considerable progress in assembling models for the biosynthesis of its two major components, the polymer cutin and cuticular waxes. The past decade has seen considerable progress in assembling models for the biosynthesis of its two major compone.
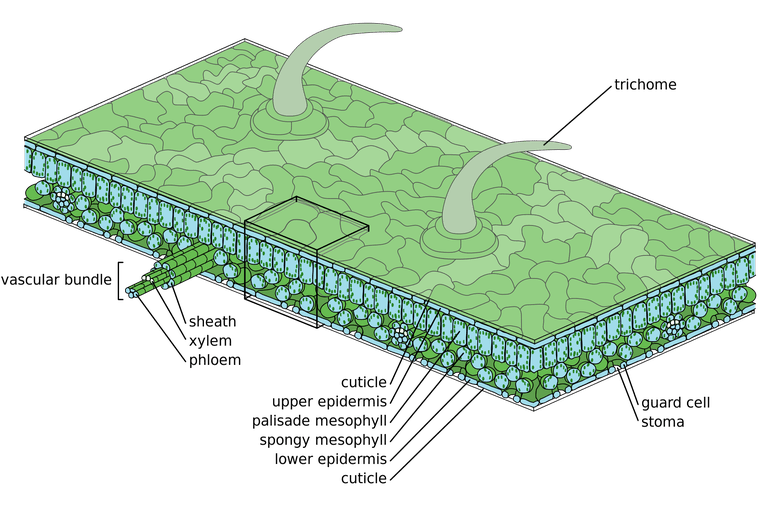 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
The past decade has seen considerable progress in assembling models for the biosynthesis of its two major components, the polymer cutin and cuticular waxes. Rose* department of plant biology, cornell university, ithaca, new york 14853 the plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection against desiccation and external environmental stresses. A) carbohydrates and oxygen b) sugar and carbon dioxide c) starch and carbon dioxide d) chlorophyll and radiant energy 4. Its prevents water loss and contamination of the plants tissue with external water, dirt and microorganisms. Recent progress in the biochemistry and molecular biology of cuticle synthesis and function highlights major questions that will drive future research in this field.
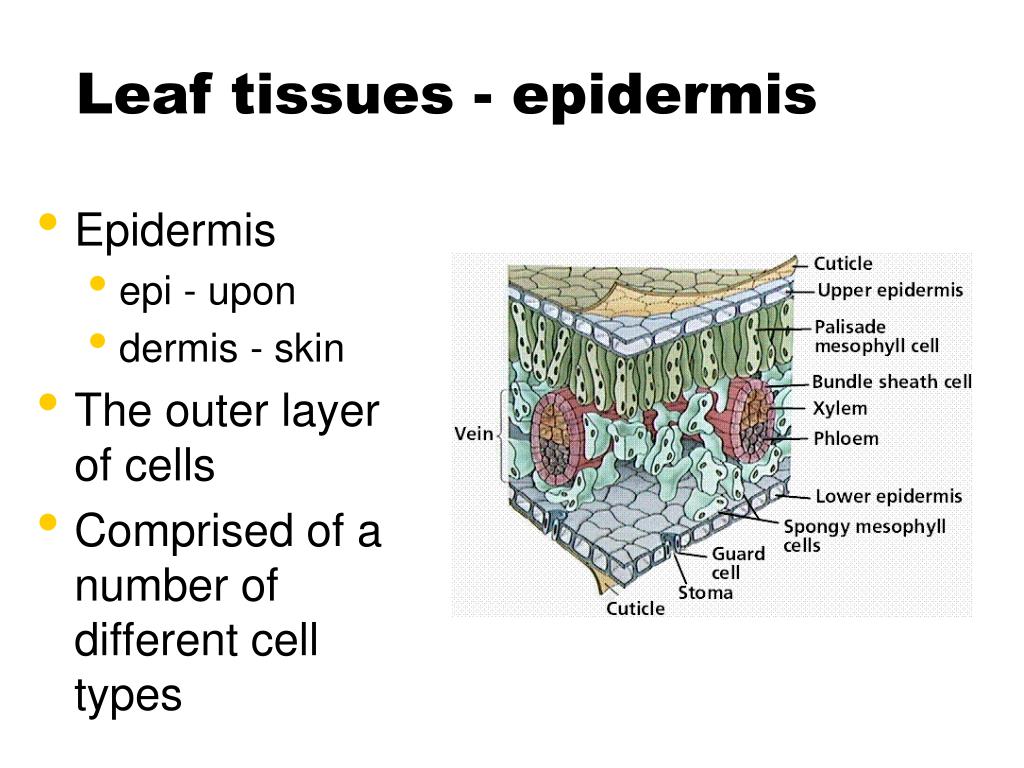 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
It protects plants against drought, extreme temperatures, uv radiation, chemical attack, mechanical injuries, and pathogen/pest infection. Cuticle thickness varies, depending on plant type and the plant parts it covers. Some plants have adapted to have a cuticle, which is the waxy layer covering the surface of the plant. Rose* department of plant biology, cornell university, ithaca, new york 14853 the plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection against desiccation and external environmental stresses. Topical review on cuticle synthesis and function the formation and function of plant cuticles1 trevor h.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The formation and function of plant cuticles1. In all types of plants, the cuticle is the layer of wax and cutin that covers the outermost surfaces of a plant. The past decade has seen considerable progress in assembling models for the biosynthesis of its two major compone. Function of cuticle in plants accounting courses near me family and friends day activities how much is $50,000 a year per month function of cuticle in plants home To see more answers head over to college study guides.
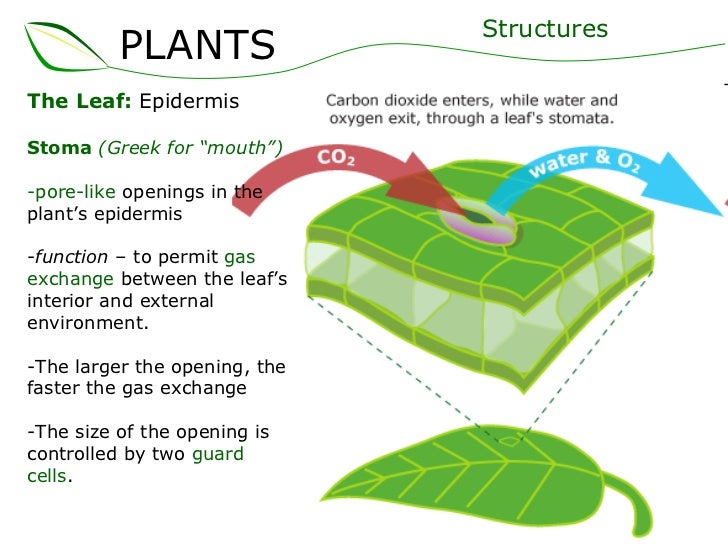 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
What is the main function of cuticle in plants brainly? Rose* department of plant biology, cornell university, ithaca, new york 14853 the plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection against desiccation and external environmental stresses. The plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection. The cuticle reduces the rate of water loss from the leaf surface. Its prevents water loss and contamination of the plants tissue with external water, dirt and microorganisms.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The formation and function of plant cuticles1. A waxy layer known as the cuticle covers the leaves of all plant species. The cuticle of nelumbo nucifera have ultra hydrophobic and. 15 the formation and function of plant cuticles trevor h. The cuticle protects the underlying tissues commonly found on the leaves of plants from rays of the sun and other.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Its prevents water loss and contamination of the plants tissue with external water, dirt and microorganisms. What is the main function of cuticle in plants? Rose� department of plant biology, cornell university, ithaca, new york 14853 the plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection Leaf name description function cuticle thin waxy layer on the epidermis reduces water loss upper epidermis thin and transparent cells with no chloroplasts present allow light to pass through prevent microorganisms from entering (barrier to disease) helps keep leaf’s shape palisade mesophyll long with many chloroplasts main region for photosynthesis chloroplast. Some plants have adapted to have a cuticle, which is the waxy layer covering the surface of the plant.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The cuticle is widely discharged by the epidermis and helps in preventing water loss and infection by parasites. The cuticle reduces the rate of water loss from the leaf surface. The plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection against desiccation and external environmental stresses. The cuticle is widely discharged by the epidermis and helps in preventing water loss and infection by parasites. It also prevents external water and solutes from entering the tissues.
 Source: carlsonstockart.com
Source: carlsonstockart.com
Topical review on cuticle synthesis and function the formation and function of plant cuticles1 trevor h. What are the functions of the cuticle and stomata? The plant cuticle is an extracellular hydrophobic layer that covers the aerial epidermis of all land plants, providing protection. Leaf name description function cuticle thin waxy layer on the epidermis reduces water loss upper epidermis thin and transparent cells with no chloroplasts present allow light to pass through prevent microorganisms from entering (barrier to disease) helps keep leaf’s shape palisade mesophyll long with many chloroplasts main region for photosynthesis chloroplast. 15 the formation and function of plant cuticles trevor h.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title function of cuticle in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.