Your How do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1 images are ready in this website. How do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1 are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the How do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1 files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for how do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1 pictures information linked to the how do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1 interest, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website always gives you hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
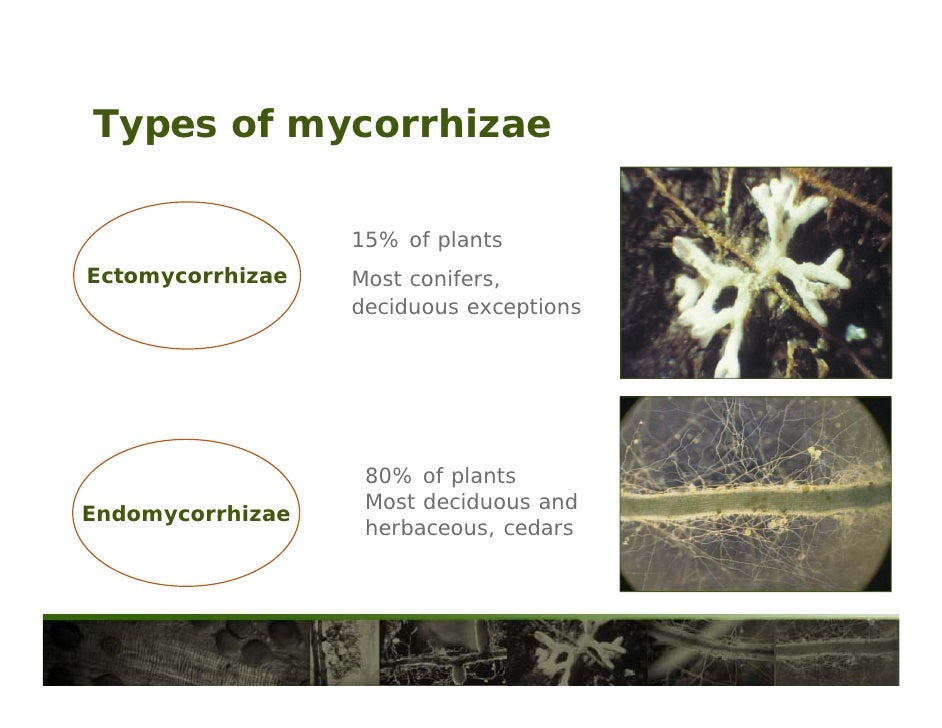
How Do Mycorrhizal Fungi Benefit Plants Site 1. In total, mycorrhizal fungi benefit 80 to 90 percent of all plant species. The fungi attach itself to the root system and help to increase the mass of the plant’s root system. Mycorrhizal fungi live in a mutually beneficial relationship with plants. Ectomycorrhizal fungi, which account for about 3 percent of mycorrhizhae, are more advanced and benefit mainly woody and tree species (table 2).
 Mycorrhizae Benefits Atul Nayar Mon Jan 25 At 2 From slideshare.net
Mycorrhizae Benefits Atul Nayar Mon Jan 25 At 2 From slideshare.net
Mycorrhizae also help the plant resist infection by other fungi and even bacteria. Mycorrhizal fungi help plants to increase their capacity for absorption. The main benefit mycorrhizal fungi provide is access to large amount of water and nutrients (particularly nitrogen, phosphorus, zinc, manganese and copper). Mycorrhizal fungi helps plants as they work synergistically with the plant to provide additional water and nutrients that the plant’s root system would not be able to reach alone. Plant roots do not sit alone in the soil. They are often selling their own brand of additive so there may be some bias here.
Their name is derived from structures they form within the plant root cell:
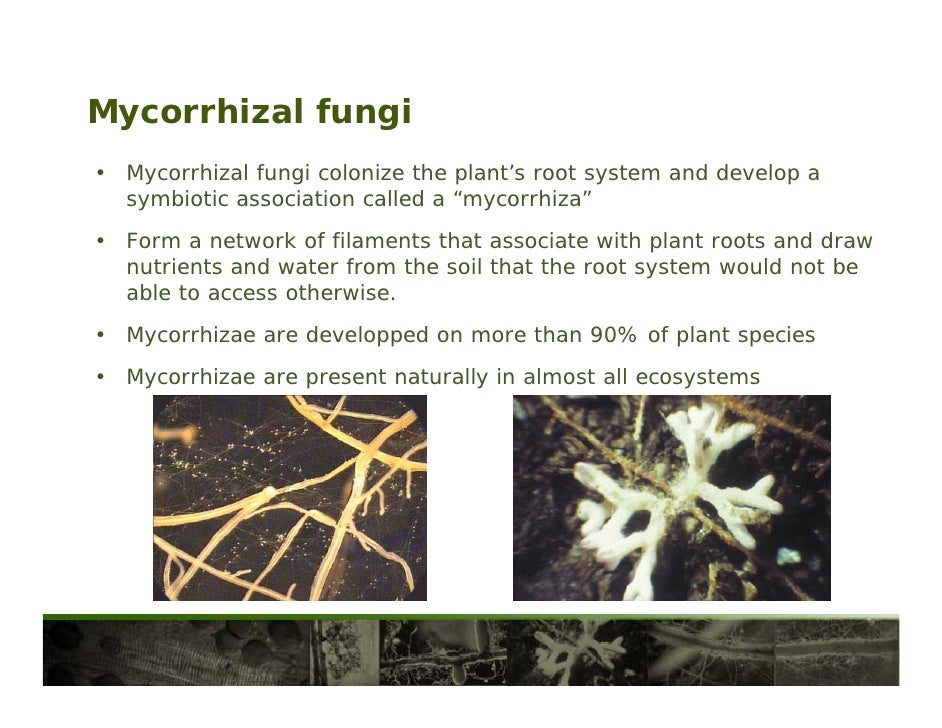
Endomycorrhizal fungi benefit not only a large number of desert plants, but a majority of the plants in the world (table 1). In total, mycorrhizal fungi benefit 80 to 90 percent of all plant species. Mycorrhizal associations benefit both the fungus and the plant by the fungus getting organic compounds such as sugars and amino acids from plants. Endomycorrhizae, or vescular arbuscular mycorrhiza (vam for short), form symbiotic relationships, sometimes called mutually beneficial relationships, with about 90% of plants. These microscopic fungi help make soils more fertile and alive. Many plant breeders and gardening experts recommend the use of mycorrhizal fungi when putting in a new plant.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
There are many types of mycorrhizal associations: In total, mycorrhizal fungi benefit 80 to 90 percent of all plant species. Mycorrhizal fungi live in a mutually beneficial relationship with plants. Annuals in planters or flower beds: The growth of plants capture of solar energy gas exchange in leaves water absorption in roots
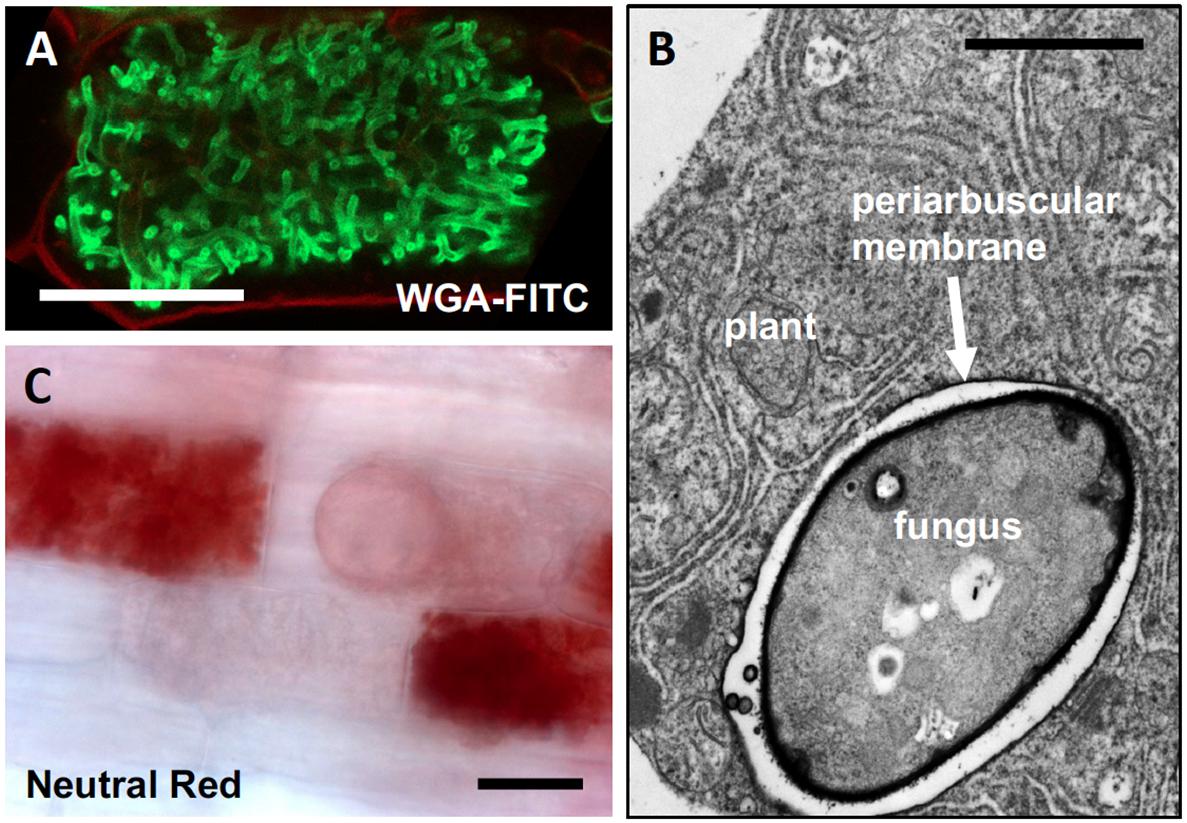 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Mycorrhizal fungi live in a mutually beneficial relationship with plants. Plant roots do not sit alone in the soil. Mycorrhizae also help the plant resist infection by other fungi and even bacteria. This is because the hyphae increase the root surface area of absorption from soil. Endomycorrhizal fungi benefit not only a large number of desert plants, but a majority of the plants in the world (table 1).
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Perception is the central processing of sensory stimuli into a meaningful pattern. How do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1 quizlet? Mycorrhizae are the mutualistic association between fungi and roots of plants. Arbuscular mycorrhizas, ectomycorrhizas, orchid mycorrhizas, and ericaceous mycorrhizas. Moreover, these fungi play a major role in soil aggregation process and stimulate microbial activity.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
The fungi attach itself to the root system and help to increase the mass of the plant’s root system. In the image (credit le micorrize e le simbiosi delle società vegetali ) you can see the simple graphical representation. Lurking in the dirt is rhizophagus irregularis, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus that colonises wheat.in a new study hui tian and colleagues investigated if what happened before a fungus makes contact with the wheat roots. Ad our houseplants are available in plastic grower pots or stunning ceramic pots. These microscopic fungi help make soils more fertile and alive.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
How do mycorrhizal fungi help plants? The growth of plants capture of solar energy gas exchange in leaves water absorption in roots Amend to the drip line cover well and/or mulch. Lurking in the dirt is rhizophagus irregularis, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus that colonises wheat.in a new study hui tian and colleagues investigated if what happened before a fungus makes contact with the wheat roots. Mycorrhizal fungi live in a mutually beneficial relationship with plants.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
This is because the hyphae increase the root surface area of absorption from soil. The fungal partner collects minerals from the remotest areas by their hyphae and supplies to the plant. These microscopic fungi help make soils more fertile and alive. Amend to the drip line cover well and/or mulch. Among the types of endomycorrhizal fungi, arbuscular mycorrhizal (am) fungi are the most prevalent in soils.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Onion, garlic, carrots, potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, cucurbits, asparagus, herbs and lettuce. It pulls starches and sugars from the plant so that the mycorrhizae can stay alive. Perhaps most bizarrely of all, the common mycorrhizal network can also serve as a means for plants to “talk ” to each other—an internet made out of fungus! The fungus is able to complete its life cycle, the plant improves nourishment, growth, resistance to disease. It may also be that the large physical presence of one fungus impedes infection by others.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Ad our houseplants are available in plastic grower pots or stunning ceramic pots. Mycorrhizal association is symbiotic association between plants and fungi, where both the partners are benefitted from each other. In total, mycorrhizal fungi benefit 80 to 90 percent of all plant species. Due to the large surface area of fungal hyphae and because hyphae are longer than plant root hairs, mycelium has a higher absorptive capacity for water and mineral nutrients than plant. Some fungi can also mobilize soil minerals that are inaccessible to the roots of the plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In return, the fungus allows the plant to better absorb water and minerals. Almost 80% of terrestrial plants have symbiotic associations with mycorrhizae fungi (sylvia, 2005). The main benefit mycorrhizal fungi provide is access to large amount of water and nutrients (particularly nitrogen, phosphorus, zinc, manganese and copper). I try to think pragmatically and pick and choose when it will do the most benefit. There are over 200 species of arbuscular.
 Source: extension.sdstate.edu
Source: extension.sdstate.edu
Endomycorrhizae, or vescular arbuscular mycorrhiza (vam for short), form symbiotic relationships, sometimes called mutually beneficial relationships, with about 90% of plants. This may be because the plant, being better nourished, is healthier and has better resistance to the invader. The growth of plants capture of solar energy gas exchange in leaves water absorption in roots In total, mycorrhizal fungi benefit 80 to 90 percent of all plant species. In total, mycorrhizal fungi benefit 80 to 90 percent of all plant species.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Explore our range of fantastic plants that are delivered straight to your door. Cultivate and blend into soil and make sure to water in well. The growth of plants capture of solar energy gas exchange in leaves water absorption in roots Hyphae bring moisture and nutrients to. Moreover, these fungi play a major role in soil aggregation process and stimulate microbial activity.
 Source: davidsgiantvegetables.com
Source: davidsgiantvegetables.com
How do mycorrhizal fungi help plants? How do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1? Endomycorrhizal fungi benefit not only a large number of desert plants, but a majority of the plants in the world (table 1). Which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi? A majority of plant species will benefit from mycorrhizal fungi urban vegetable crops in soil or trays:
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Many plant breeders and gardening experts recommend the use of mycorrhizal fungi when putting in a new plant. This gives the mycorrhizal fungi time to colonize your plants root mass and ensure a successful grow. In total, mycorrhizal fungi benefit 80 to 90 percent of all plant species. The fungus is able to complete its life cycle, the plant improves nourishment, growth, resistance to disease. In the image (credit le micorrize e le simbiosi delle società vegetali ) you can see the simple graphical representation.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It pulls starches and sugars from the plant so that the mycorrhizae can stay alive. How do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1? Mycorrhizal associations benefit both the fungus and the plant by the fungus getting organic compounds such as sugars and amino acids from plants. Moreover, these fungi play a major role in soil aggregation process and stimulate microbial activity. This may be because the plant, being better nourished, is healthier and has better resistance to the invader.
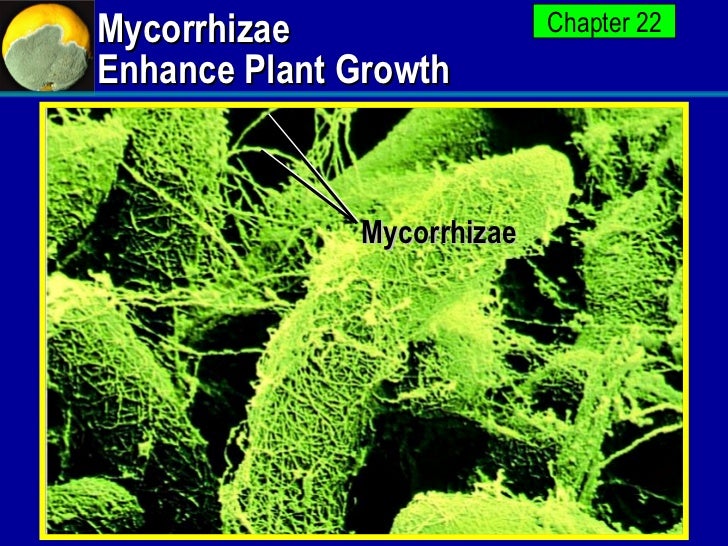 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Perception is the central processing of sensory stimuli into a meaningful pattern. In return, the fungus allows the plant to better absorb water and minerals. Ad our houseplants are available in plastic grower pots or stunning ceramic pots. The fungal partner collects minerals from the remotest areas by their hyphae and supplies to the plant. Lurking in the dirt is rhizophagus irregularis, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus that colonises wheat.in a new study hui tian and colleagues investigated if what happened before a fungus makes contact with the wheat roots.
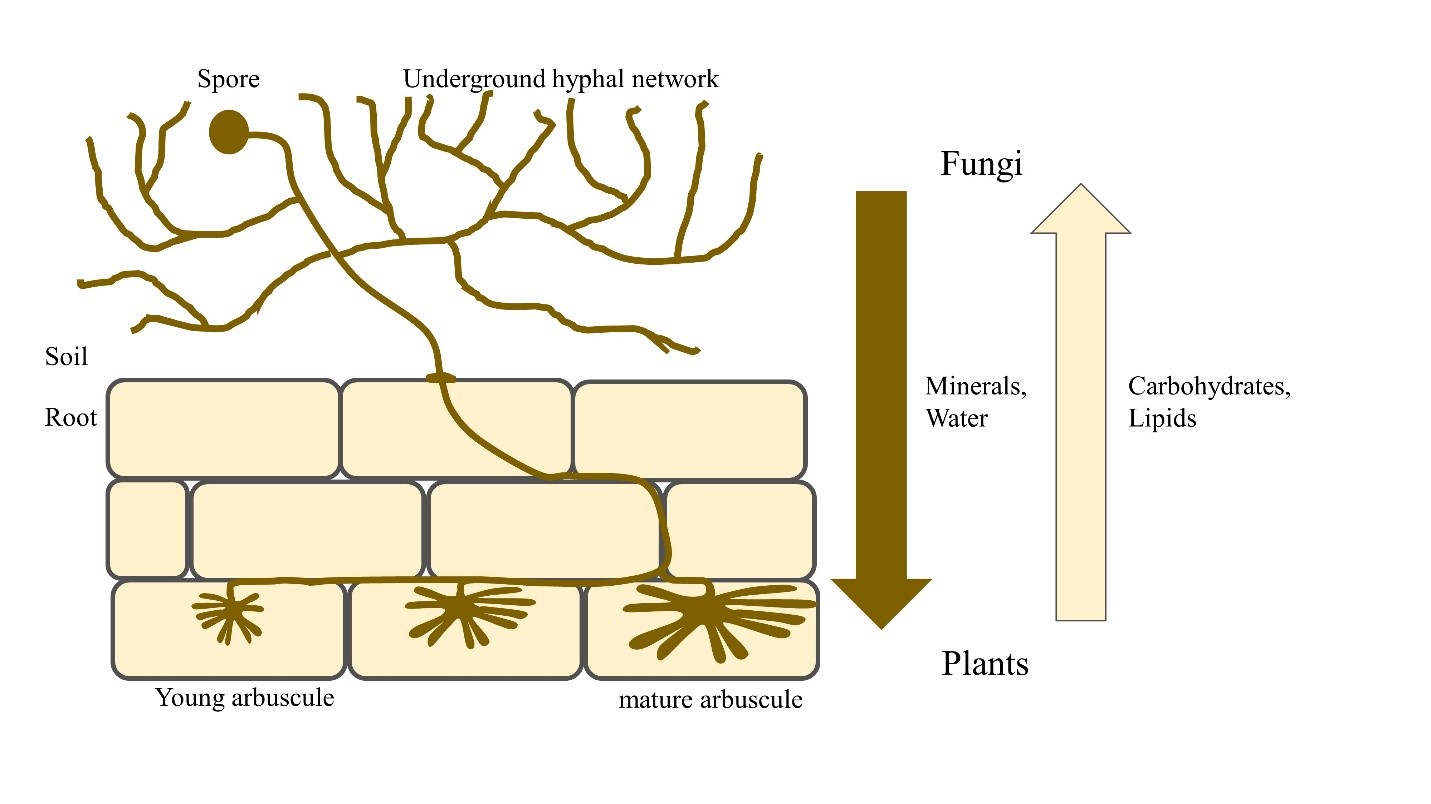 Source: turf.umn.edu
Source: turf.umn.edu
Perception is dependent on sensation, but not all sensations are perceived. Their name is derived from structures they form within the plant root cell: Almost 80% of terrestrial plants have symbiotic associations with mycorrhizae fungi (sylvia, 2005). The fungal partner collects minerals from the remotest areas by their hyphae and supplies to the plant. Explore our range of fantastic plants that are delivered straight to your door.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The mycorrhizas are a particular type of symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant, located in the roots of the plant. It pulls starches and sugars from the plant so that the mycorrhizae can stay alive. This relationship is thought to date. Mycorrhizae can also serve as a sugar delivery service when plants shuttle sugar back and forth to different plants connected to the same common mycorrhizal network. Perception is the central processing of sensory stimuli into a meaningful pattern.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Mycorrhizae are the mutualistic association between fungi and roots of plants. The fungi attach itself to the root system and help to increase the mass of the plant’s root system. Ectomycorrhizal fungi, which account for about 3 percent of mycorrhizhae, are more advanced and benefit mainly woody and tree species (table 2). Lurking in the dirt is rhizophagus irregularis, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus that colonises wheat.in a new study hui tian and colleagues investigated if what happened before a fungus makes contact with the wheat roots. Granular mycorrhizae and biostimulants are also beneficial to apply to established plants.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how do mycorrhizal fungi benefit plants site 1 by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






